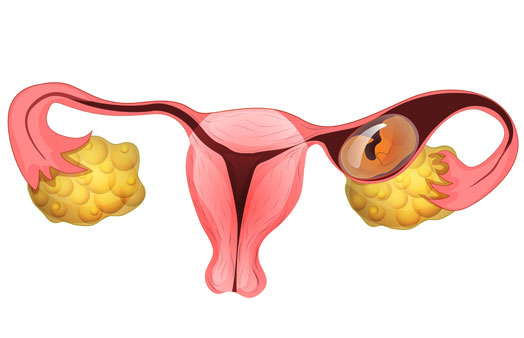
What is an ectopic pregnancy?
In a normal pregnancy, a fertilised egg travels to the uterus via a fallopian tube. The egg adheres to the uterus and begins to develop. An ectopic pregnancy, on the other hand, occurs when the fertilised egg attaches (or implants) somewhere other than the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tube. In rare situations, the egg implants in the ovary, cervix or abdomen.
An ectopic pregnancy is an emergency requiring immediate action, the pregnancy cannot be allowed to continue. If the egg continues to grow in the fallopian tube, it might damage or burst the tube, causing severe bleeding that can be fatal. If you have an ectopic pregnancy, you will require immediate treatment to end it before it causes serious complications.
What is the cause of an ectopic pregnancy?
An ectopic pregnancy usually occurs when a fertilised egg is unable to move quickly down the fallopian tube into the uterus. A tube infection or inflammation could have partially or completely blocked it. A prominent cause of fallopian tube obstruction is pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which can be caused by gonorrhea or chlamydia, Pelvic tuberculosis.
Other Risk factors include, previous surgeries, pregnancy that has occurred with an IUD, smoking.
Endometriosis and scar tissue from past abdominal or fallopian procedures can also create obstructions. Birth malformations, on the other hand, might alter the shape of the tube and impede the development of the egg.
What are the signs and symptoms?
An ectopic pregnancy usually causes the same symptoms as a normal pregnancy in the first few weeks, such as a missing menstrual period, exhaustion, nausea, and breast pain.
The following are the primary symptoms of ectopic pregnancy:
Pain in the lower abdomen or pelvis. It may start sharp on one side and gradually spread throughout your belly. It could get worse if you move or strain.
Heavy vaginal bleeding
If you suspect you’re pregnant and are experiencing these symptoms, see your doctor immediately.
How is an ectopic pregnancy diagnosed?
A urine test can determine whether or not you are pregnant.
A pelvic examination to determine the size of your uterus and to feel for growths or pain in your abdomen.
A blood test is used to determine the level of the pregnancy hormone (hCG). This test is carried out again two days later. During the earlier weeks of pregnancy, the level of this hormone doubles every 48-72hrs. Low levels indicate an issue, such as an ectopic pregnancy.
Ultrasonography. This examination can produce images of what is inside your stomach. A doctor can generally detect a pregnancy in the uterus using ultrasound 6 weeks following your last menstrual cycle.
What is the treatment for an ectopic pregnancy?
Ectopic pregnancy in its early stages
After diagnosis, your doctor will go over your treatment options with you, and in many circumstances, you will be able to choose the best option for you. Among these are the following:
If the pregnancy is discovered early, before the tube is destroyed, medicine can be administered. In most situations, one or more shots of methotrexate, a medication, will end the pregnancy. Although taking the shot allows you to avoid surgery, it may have some negative effects. You will need to see your doctor for follow-up blood testing to ensure that the shot was effective. Misoprostol (intravaginally) has been extensively investigated for its usage in obstetrics and has proven to be effective to treat ectopic pregnancy.
Surgery. Keyhole surgery is most usually used to remove the tube (either the entire tube or a portion of it) along with the product of conception. If the other tube is healthy, the Fallopian tube holding the ectopic pregnancy is usually removed (salpingectomy). If the other tube is already damaged, a salpingotomy (removal of only a piece of the tube containing the ectopic pregnancy) is frequently performed.
Ectopic pregnancy rupture
If a Fallopian tube splits (ruptures) with significant bleeding, emergency surgery is required. The primary goal is to control the bleeding. The ruptured Fallopian tube and early pregnancy remnants are then removed. The procedure is often life-saving. Any emergency during your pregnancy contacts our emergency care.
If you have any complications during your pregnancy, get an appointment with Dr.ANSHUMALA SHUKLA who is the best gynecologist in Mumbai to treat all kinds of problems that may occur during pregnancy.
