Mullerian Anomalies
Mullerian Anomalies are classified as a ‘congenital condition,’ which means they develop throughout foetal development and are present at birth. As an embryo grows, two paired müllerian ducts develop into the female reproductive system, which comprises the fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and upper two-thirds of the vagina. When this system is disrupted, a wide range of abnormalities can result. Mullerian abnormalities affect up to 4% of females.
Causes of mullerian anomalies
Müllerian abnormalities are caused by a variety of factors. Some may be inherited, while others may be the result of a chance gene mutation or developmental defect.
Types of Müllerian Anomalies
Types of Mullerian anomalies include the absence of a uterus, the formation of a half or double uterus, and the division of a uterus by a septum. All types have a varied degree of impact on the reproductive tract. They are as follows:
Agenesis & Hypoplasia
Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser syndrome is the most common cause of agenesis and hypoplasia. The Müllerian tract fails to form completely or is severely underdeveloped.
Unicornuate uterus (UU)
A banana-shaped half-uterus is generated when one müllerian duct is undeveloped or fails to develop. This asymmetric aberration is more likely to be accompanied by a missing kidney or other kidney problems than by other müllerian malformations. This is a very uncommon condition.
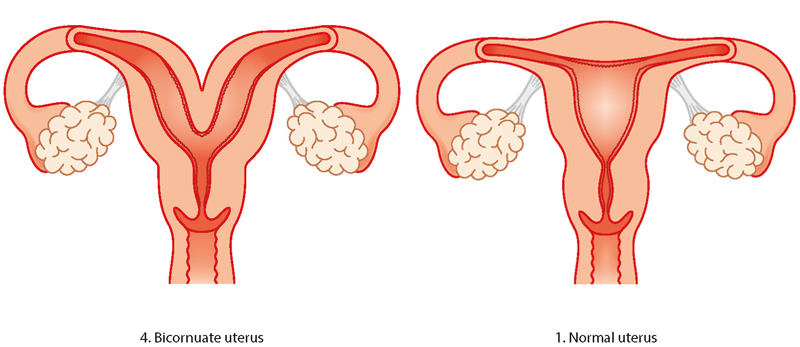
Uterus didelphys (UD)
Also known as a “double uterus.” The vagina, cervix, and uterus may be completely duplicated, and the two parts may be separated by a connective tissue ligament. Among all MAs, UD had the best pregnancy outcomes. The most common type of müllerian abnormality is a bicornuate uterus (BU). It’s been described as a womb with two horns. The womb is not pear-shaped, but rather heart-shaped, with a deep indentation at the top. This means that the baby has less chance to expand than if the womb were regularly formed.
Septate uterus
This condition occurs when the interior of the uterus is split by a wall or septum. The septum may extend either partially into the uterus or it may reach the cervix.
DES-related uterus
This anomaly is distinguished by a T-shaped uterine cavity, dilated horns, and a deformed cervix and upper vagina. A T-shaped uterus is sometimes caused by maternal ingestion of DES, but the etiology is not always known.
Arcuate uterus (AU)
The fundus of the uterus might be slightly indented on both the inside and outside.
How are Müllerian anomalies diagnosed?
Mullerian anomalies are frequently identified around the commencement of puberty – when an adolescent begins to menstruate or when a young female does not have her menstrual cycle. When a woman has difficulty conceiving or maintaining a pregnancy, she may be diagnosed with the syndrome. Some defects are connected with stomach or pelvic pain, sex discomfort, or menstruation irregularities.
Imaging technologies can detect and diagnose a müllerian abnormality as well as other current reproductive problems. Diagnostic testing may involve the following:
Ultrasonography of the pelvis, Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and laparoscopy with a hysterosalpingogram (HSG) hysteroscopy help in the diagnosis of Mullerian Anomaly.
To make the most accurate diagnosis, a combination of tests may be recommended.
What is the treatment for Mullerian anomalies?
Mullerian malformations that impact fertility, such as a septate uterus (a partitioned uterus), can be repaired, improving the chance of a future pregnancy. Women who have congenital reproductive abnormalities and have not been able to conceive within six months of attempting should consult a fertility expert who specialises in reproductive surgery. Surgery can correct the abnormality, alleviate pain during menstruation, and improve fertility and pregnancy results.
In many circumstances, the illness can be left untreated, especially if it does not have a significant impact on reproduction. Mullerian abnormalities that inhibit menstruation or cause substantial pain are typically corrected surgically. Surgical intervention is decided on the severity of the individual problem.
For infertility treatment, book your appointment today with Dr. ANSHUMALA SHUKLA, who is a renowned gynecologist with experience in treating infertility cases.
